
Each of these stationary states is characterised by a specific amount of energy called its energy level. Therefore, each atom must be able to exist with only certain specific values of internal energy. During the emission of a photon, the internal energy of the atom changes by an amount equal to the energy of the photon. Planck’s hypothesis that energy is radiated and absorbed in discrete “quanta” (or energy packets) precisely matched the observed patterns of blackbody radiation and resolved the ultraviolet catastrophe.īased on this hypothesis, Bohr postulated that an atom emits or absorbs energy only in discrete quanta corresponding to absorption or radiation of a photon. Planck’s law is a pioneering result of modern physics and quantum theory. Planck’s quantum hypothesis ( Planck’s law) is named after a German theoretical physicist Max Planck, who proposed it in 1900. The Bohr model adopted Planck’s quantum hypothesis and he proposed a model in which the electrons of an atom were assumed to orbit the nucleus but could only do so in a finite set of orbits.
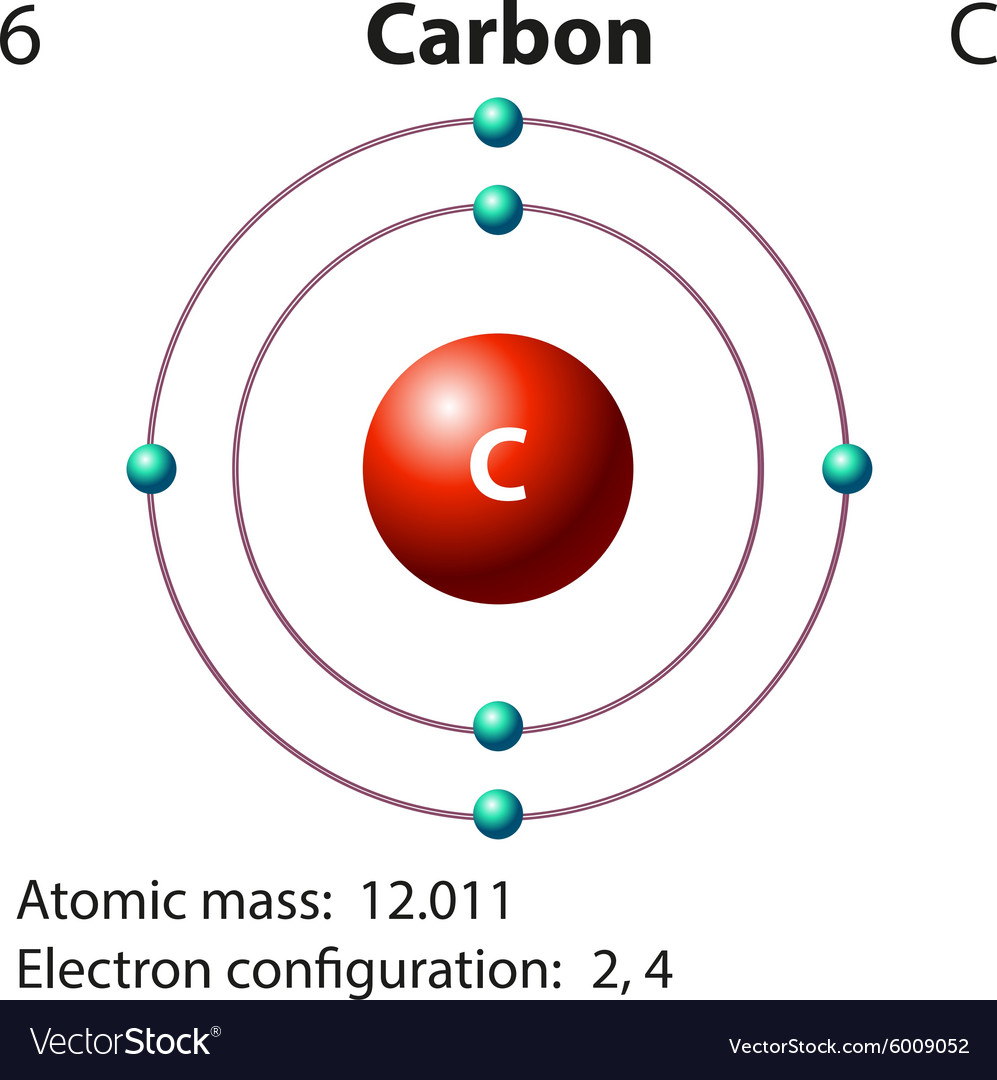

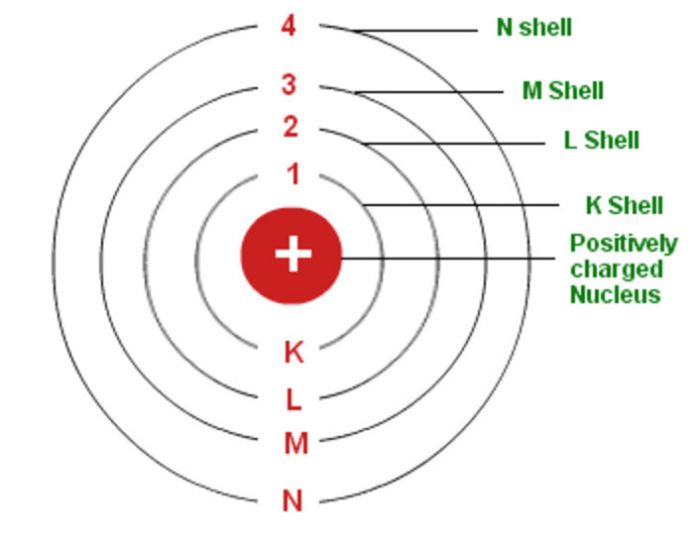
In atomic physics, the Bohr model if the atom (also known as the Rutherford-Bohr model) is modern model of the hydrogen atom introduced by Danish physicist Niels Bohr working with Ernest Rutherford at the University of Manchester in 1913.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
